Mining has always been an industry filled with inherent risks, from the dangers posed by unstable underground environments to the challenges of managing large workforces in remote locations. With the transformation of the industry comes the role of technology in altering the safety strategy, with technological innovation being central to it. Technology offers new ways to not only lower risk but also drive efficiencies in operations. This, in turn, leads to safe working environments. Whether through applications or monitoring technologies, the development of mining safety technology represents a fundamental shift to being proactive and data-driven in terms of risk management.
We cannot say enough about the importance of these technological developments. They allow mining companies to identify hazards before they become an incident, maintain standards in safety, and create a culture of safety. With the growing regulatory pressures and stakeholder demands, the use of mining safety technology becomes imperative for safe and responsible mining activities.
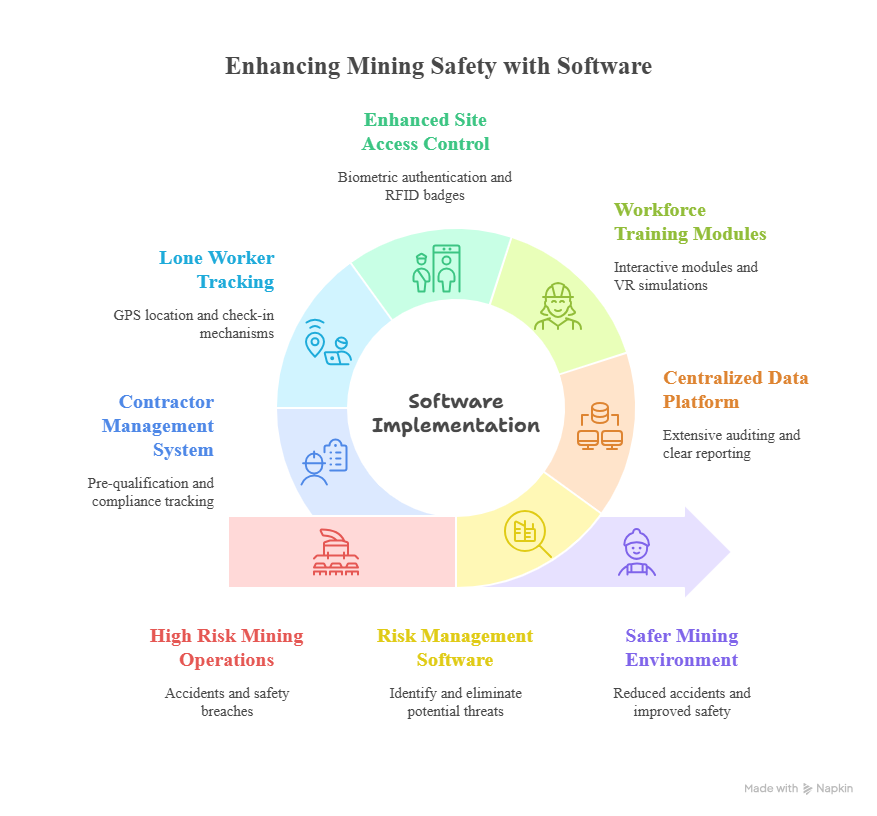
Software Applications for Mining Safety
The deployment of specialized software applications has transformed safety management in the mining industry. These programs offer an integrated platform for risk analysis, incident reporting, and operational monitoring. Their integration into regular activities enables a move towards proactive rather than reactive safety measures.
The use of specialized software applications has radically changed safety management in the mining sector. The software allows mining firms to anticipate potential hazards, automate compliance procedures, and create a safer work environment by analyzing real-time data insights and automation. By incorporating these applications into everyday operations, mining companies can minimise accidents, enhance operating efficiency, and guarantee regulatory compliance.
-
Risk Management and Hazard Prevention
Risk management software is essential for identifying and eliminating potential threats to the site before an actual incident occurs. This software uses instantaneous feeds from sensors embedded in the equipment and from environmental monitoring systems to analyse such factors as gas levels, structural stability, temperature, and equipment vibration. Advanced analytics compare the data to standardized patterns and will look for deviations that may foreshadow physical harm.
For example, when sensors identify toxic gas levels increasing in an underground tunnel, the software immediately sends a signal to the site Managers and activates a response protocol to evacuate/ventilate. This type of preparation enables a site to simplify and execute a protocol to reduce the odds of an accident and eliminated health risks to workers. Additionally, digital risk assessment tools enable ongoing hazard evaluations, facilitating continuous safety improvements aligned with industry best practices and regulatory standards.
-
Centralising Data for Auditing and Reporting
Centralization of safety data is one of the greatest benefits of contemporary safety software. It allows for extensive auditing and clear reporting of the data. Rather than depending on paper logs, manual records, and separated spreadsheets, electronic platforms merge all safety-related data into a single database.
This centralised database provides simple access to historical incident reports, inspection records, maintenance logs, and safety audits. Real-time visibility into safety performance metrics is provided through automated dashboards, enabling the management to simply notice trends, bottlenecks, or repeated problems. This transparency facilitates regulatory compliance, streamlines audit processes, and enables data-driven decision-making for constant safety improvements.
In addition, centralised reporting systems facilitate incident investigation by presenting clear timelines, photographs, sensor logs, and witness statements, thereby allowing accurate root cause analysis and preventative action planning.
-
Workforce Education and Training
Understanding safety in the workforce is vital in reducing accidents and ensuring safe work practices. The software programs that exist today include interactive online modules, virtual reality (VR) simulations, and web-based training portals to accommodate different roles within the mine system. These systems support standardized dissemination of safety procedures and protocols irrespective of location or shift schedules.
For example, virtual reality-based training enables workers to undergo virtual-risky situation simulations so that they can gain the ability to make instant decisions in a safe environment. Computer-based training modules track employee learning, understanding levels, and certification status so that the training can alert all employees to the safety protocols. The software also supports the on-boarding of workers and contractors with a commitment to safety from day one.
-
Enhancing Site Access for Safety and Security
Access control to risk areas is essential for ensuring safety and security at mining operations. Applications now include biometric authentication, RFID badge systems, and facial recognition capabilities to verify personnel before allowing site access. These systems are very detailed access logs, and are incredible to help audits and incident investigation.
Simplified access site systems often have geofencing abilities to verify that employees are in a specific area in the facility. If there is an unauthorised access point or an intrusion, alerts are sent immediately to initiate response action. These measures keep unauthorized staff from entering risky areas, thus minimizing risk exposure and avoiding accidents due to unqualified or unauthorised staff.
-
Tracking Lone Workers for Enhanced Safety
Many mining operations involve workers operating independently in isolated sections of a site, which increases their vulnerability in case of emergencies. Current safety applications have mitigated the risk using GPS location-enabled tracking devices and automated check-in mechanisms. Lone workers wear devices or mobile apps that send location information to a centralised monitoring system.
When an employee doesn’t check-in within a scheduled time or indicates signs of distress (e.g., sudden idleness or irregular vital signs picked up via biometric sensors), automated notification is sent to supervisors. Rescue teams can then rapidly find and attend to the worker, reducing the potential for extended exposure to harm. This mining safety technology not only increases individual safety but also increases feelings of security, prompting workers to work confidently in remote or risky areas.
Managing Contractors for Improved Safety
Contractors play a crucial role in mining operations, but their transient population and differing safety practices create special challenges. Proper handling of contractors through technological means guarantees that the safety standards are maintained in all outside dealings, minimising the exposure to risk and maintaining a safety-oriented atmosphere.
-
Pre-qualification and Compliance Tracking
Before contractors are authorized to work on site, it is necessary to assess their safety history, qualifications, and compliance. Pre-qualification software helps mining companies evaluate the contractor’s compliance using defined safety criteria such as safety incident history, safety certifications, and insurance. Such software automates the validation process, with rigorous vetting before approval.
Upon arrival at the site, compliance monitoring devices continuously monitor contractor compliance with safety protocols using electronic checklists, incident reports, and audit trails. Automatic alerts notify management of safety slip-ups so that immediate corrective measures can be taken. Through this proactive monitoring, all contractors work within the safety framework of the organization, drastically minimizing the risk of accidents due to poor safety practices.
-
Onboarding and Safety Inductions
Contractor onboarding is a pivotal time when safety culture is developed. Online onboarding solutions provide standardized safety inductions via e-learning modules, videos, and virtual reality training. These resources guarantee uniform messaging and thorough comprehension of safety procedures, even for contractors employed in multiple locations or locations.
Monitoring for completion and understanding tests ensures that contractors are sufficiently trained before starting work. This electronic method streamlines paperwork, accelerates onboarding, and assures that safety is embedded from the initial day on-site. Online portals can also offer contractors web access to safety manuals, emergency response instructions, and contact details, and encourage ongoing interaction with safety processes.
-
Real-Time Contractor Monitoring
Remote monitoring of contractor activity improves surveillance and accountability. Biometric sensors and GPS-enabled wearable devices on workers offer real-time location, activity, and vital sign data. Managers can monitor live dashboards of where contractor staff members are, making sure they work in authorized areas and follow safety procedures.
Automatic alerts notify management when a contractor enters restricted areas, does not check-in, or shows behavior that could be caused by stress. It is this real-time feedback loop that includes the ability to intervene, either verbally or by calling emergency services, in a streamlined manner. It is this kind of monitoring and notification that prevents accidents and creates a culture of safety responsibility with the contractors, making sure they operate as company safety procedures require.
Conclusion
The new approach to use of technology throughout mining safety practices represents a unique opportunity for the industry. Movements from reactive, typical approach practices to predictive, data-based processes that can significantly decrease incidents, and save lives. Risk management software applications, and databases, and online training tools for workers have become key ingredients used in this revolution, while paving the way for making mines safer.
Moreover, in combination with contractor management through pre-qualification, hiring, and real-time monitoring, assurance of safety standards are being considered from every angle of the operation. Not only are these types of proactive technologies ensuring the safety of workers, but improving operational efficiency, compliance with regulations, and increasing stakeholder confidence.
Moving forward, mining safety in the future will undoubtedly change as we continue to see additional technologies emerge in the form of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and Internet of Things devices. These types of technologies provide the pathway to higher standards for safety, automation, and accuracy as high as possible relatively to the highest safety standards. As the sector continues to develop and grow, the adoption of new technologies will be important and make mining a safe and sustainable sector for future generations.






















